HVDC Transmission

High Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) power systems use direct current for transmission of power over long distances. HVDC transmission is preferred over HVAC as the HVDC system is cheaper and reduces the power loss by a significant amount. Superhighway or Power Superhighway is the electrical name that is often used for HVDC.
In AC Transmission, direction of voltage and current changes continuously which causes overheating in the lines, thus resulting in significant power loss. Unlike AC transmission, current and voltage flow in one direction only in DC Transmission. So, when we convert HVAC into HVDC we observe significant reduction in power loss hence increasing the efficiency of the transmission lines.
HVDC Transmission system is the combination AC and DC system, first the generated AC voltage is converted into DC at the transmission end, when it reaches the receiving end DC is inverted to AC for distribution purposes. So, in order to carry out this operating, we need conversion devices at both ends of transmission line. However, HVDC Transmission is economical only for long distance transmission; overhead lines having a length more than 600km and underground cables of length more than 50km. Further we are going to discuss components, working, classification, comparison with HVAC system, advantages & disadvantages of a HVDC Transmission system.
Stay Sharp & Join our Mailing List!
Our surveys show that 90% of the people who join our blog have found the content valuable! Join today

Types of Sub
Components of HVDC System
Converter: Converts AC to DC and DC to AC. It consists of rectifiers and inverters.
- Rectifier: A device that converts alternating current to direct current which flows only in one direction.
- Inverter: A device that converts direct current into alternating current.
Electrodes: Conductors that are used to connect the system to the earth.
Smoothing Reactors: Smoothing reactors consist of inductors connected in series with the pole of each converter station. It prevents commutation failures experienced by inverters, reduces harmonics, and avoids breaking off the current.
DC Lines: Cables or overhead lines that carry power.
Harmonic Filters: Used to minimize the harmonics in voltage and currents of the converters used.
Reactive Power Supplies: Converters at the terminals consume reactive power from the supply, thus shunt capacitors are used to provide this reactive power compensation.
AC Circuit Breaker: Used for electrical safety ; like fault in transformers, disconnection of the DC link.
If you haven’t checked out our detailed blog on Types of Circuit Breaker and its Selection have a look here and let us know what you think.
How does HVDC Transmission System Work?
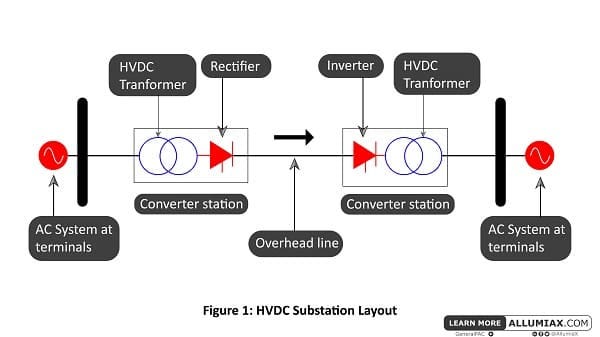
In generating substation, AC power is generated, which is converted into DC using a rectifier. The DC flows through the overhead line, and then again at the user end, DC is converted into AC using inverters and then AC is supplied to the load. Rectifiers and inverters are placed inside the converter stations at the sending and receiving ends.
As DC flows through overhead lines, the input power is equal to the output power, decreasing the losses and improving efficiency.
The diagram above shows two converter stations and one transmission line, so this type of system is known as the ‘Point-to-point system’ or ‘Two terminal DC system.’ Likewise, if there are more than two converters and the interconnecting DC terminal lines in a substation, it is named ‘Multi terminal DC substation.’
Classification of HVDC Links
HVDC links are used for connecting two networks or a system. They are classified into three types:
- Monopolar Link
- Bipolar Link
- Homopolar Link
To read the details of each category click on “HVDC Transmission”.
Comparison of HVDC and HVAC Transmission

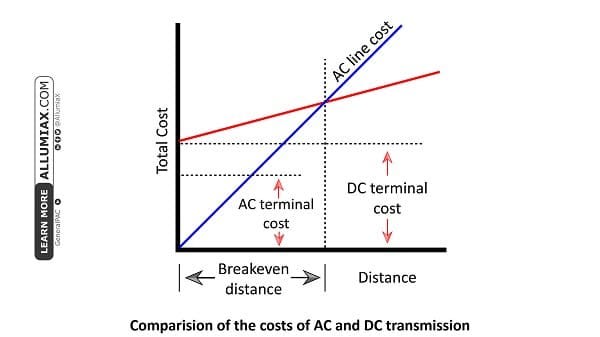
This graph shows the comparison between cost of AC and DC Transmission with respect to the distance. According to the graph, initial cost of HVDC transmission is high as compared to the HVAC Transmission due to a significant difference between DC and AC terminal cost (converter stations at terminals of HVDC Transmission system are very costly). However, at a specific distance cost of HVDC Transmission is equal to the cost of HVAC system, that point is called breakeven distance. After this point, overall cost of HVDC Transmission becomes low than HVAC Transmission (there are huge power losses in HVAC Transmission for long distances), hence proving the fact that HVDC Transmission system is economical for long distance transmission. The breakeven distance is around 600km for overhead transmission lines.
Advantages & Disadvantages of HVDC Transmissions
Advantages: This transmission requires fewer conductors and insulators, thus reduces the cost of the overall system. It requires less phase to phase and ground to ground clearance. Towers of HVDC transmission are inexpensive. Corona loss in HVDC transmission is lesser compared to the loss in power transmission lines of HVAC. Fewer lines are used for transmission of power. Therefore power loss is reduced. The HVDC system uses earth return in case of a fault in one pole. The pole with ‘earth returns’ behaves like an independent circuit, hence enhancing the system’s flexibility. HVDC system is used to interconnect two substations with different frequencies. It has an asynchronous connection between two AC stations connected using the HVDC link; thus the transmission of power is independent of sending and receiving end frequencies. Proximity and skin effect do not transpire in the system due to the absence of frequency in HVDC lines. Reactive power compensation is not needed as there is no generation or absorption of any reactive power. Power flowing through DC link is very précised and lossless.
Disadvantages: Due to installation of converter substation at both the ends, conversion from AC to DC and vice versa becomes quite expensive. Harmonics are produced by rectifiers and inverters which are reduced by using active filters, hence cost of system is increased. HVDC substation has a chance of power failure if a fault occurs in the nearby AC substation. The overload capacity of inverters used in converter substations is restricted. The circuit breakers used in HVDC are very costly. Transformers are unavailable for changing the voltage levels. Heat loss occurs in converter substations. HVDC link itself is also very complicated.
HVDC vs HVAC Transmission
Considering the advantages of HVDC transmission system we can say that it is more economical to use HVDC then HVAC but there are few disadvantages that we should consider like the initial cost of HVDC substation is quite high and the substation is very complicated. Hence, it concludes that HVDC system is preferred over HVAC system over long distance only in which power is generated in AC and then for transmission it is converted into DC, at the receiving end again it is converted back to AC for final use. Thus, we can make transmission system more economical along with improving its efficiency.
Let us know if you have any queries regarding this topic and do provide us with your feedback in the comments.
Hiring a professional electrical engineer to conduct an Arc Flash Analysis and Short Circuit Study is a great way to ensure the safety of your facility and workers against unwanted incidents.
AllumiaX, LLC is one of the leading providers of Power System Studies in the northwest. Our matchless services and expertise focus on providing adequate analysis on Arc Flash, Transient Stability, Load Flow, Snubber Circuit, Short Circuit, Coordination, Ground Grid, and Power Quality.
To learn more about AllumiaX in detail, follow us on Facebook, LinkedIn, and Twitter and stay updated with all the latest news regarding electrical engineering.
Call Us: (206) 552–8235
About The Author
Abdur Rehman is a professional electrical engineer with more than eight years of experience working with equipment from 208V to 115kV in both the Utility and Industrial & Commercial space. He has a particular focus on Power Systems Protection & Engineering Studies.
Abdur Rehman is the CEO and co-founder of allumiax.com and creator of GeneralPAC by AllumiaX. He has been actively involved in various roles in the IEEE Seattle Section, IEEE PES Seattle, IEEE Region 6, and IEEE MGA.
